Shockwave FAQs
What is a shockwave?
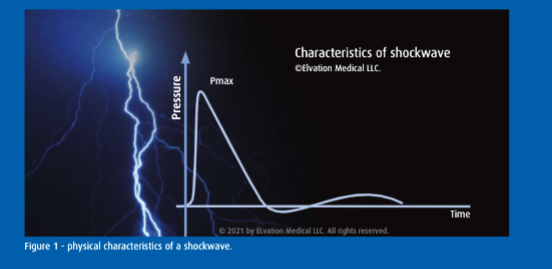
A shockwave is an acoustic wave with high peak pressure (up to and above 100 MPa) that has a short rise time of nanoseconds (steep-slope) followed by a low tensile wave. A shockwave has a small pulse width with both the high and low pressure waves occurring within 5-10 microseconds.
What is PiezoWave2-Vet shockwave and how does it differ from other focused shockwave modalities?
PiezoWave2-Vet shockwave is a therapeutic modality that uses acoustic pressure waves to target specific tissues in the body. These shockwaves are formed within the focal zone and directed toward the area of interest in the body to promote healing, pain relief, and tissue regeneration.
PiezoWave2-Vet differs from other shockwaves in the technology used to generate the shock waves. It uses a piezoelectric generator in which a transducer converts electrical energy into mechanical pressure waves. The geometry and number of piezoceramic within each transducer provides a directly focused, specific focal zone within the tissue. The energy leaves the transducer as pressure waves and steepens into the therapeutic shockwave within the tissue.
Advantages to Piezo shockwave in comparison to electrohydraulic or electromagnetic include: directly focused energy without scatter of energy off reflectors, specificity in terms of EFD and depth of penetration, biofeedback, less noise, and less stress for the patient.
What types of conditions can be treated using PiezoWave2-Vet?
PiezoWave2-Vet shockwave is used to treat both acute and chronic musculoskeletal conditions in animals. It is often used for tendinopathies, osteoarthritis, non-healing bone, myofascial pain and restrictions, and wounds.
What is the average length of treatment and typical treatment schedule?
PiezoWave2-vet treatments will vary in length depending on the size of the animal and the areas being treated. In general, treatment times range from 10-30 minutes.
A series of treatments (3-6) is recommended for tissue healing.
The frequency of treatments can be variable and dependent on the case, weekly or every 2 weeks seems favorable, but timing is dependent on each case.
What is the mechanism of action for PiezoWave2-Vet?
PiezoWave2-vet shockwave both stimulates healing and reduces pain through the mechanism of mechanotransduction, converting mechanical stimuli into biological responses.
When the shock waves reach the targeted tissue, they create mechanical stress and trigger a series of cellular reactions; including, increased blood flow, the release of growth factors, and stimulation of cell proliferation. These biological actions work together to enhance the body's natural healing processes.
The high-pressure waves can also disrupt pain pathways, reduce inflammation, and stimulate the release of substances that block pain signals. This results in decreased pain perception and improved comfort for the animal. The analgesic effect of shockwave usually lasts for about three days.
Can you extrapolate the uses of the PiezoWave2-Vet shockwave from clinical studies and other literature using electrohydraulic or electromagnetic shockwave modalities?
Yes, all focused shockwaves, electrohydraulic, electromagnetic, and piezoelectric, create shockwaves, acoustic waves with high peak pressure followed by a low-pressure wave, that act on the cells via mechanotransduction. They all initiate the same cellular responses as long as an appropriate amount of energy is delivered to the specific tissue.
.png?width=600&height=200&name=Fig.%201%20electrohydraulic%20(1).png)
However, the focal zone produced by each different shockwave varies in size, shape, and volume. It is difficult to compare the exact protocols used to treat specific conditions with different shockwave modalities. By understanding the specific shockwaves, their differences in focal zones, and the EFD (mJ/mm2) used in the clinical studies, it is possible to make educated decisions for determining a protocol for the use of the PiezoWave2-Vet when comparing to the use of either electromagnetic or electrohydraulic shockwave modalities.
