Mechanotransduction Simplified
Therapeutic shockwave use for veterinary patients provides a drug-free option to promote tissue healing and pain relief for the recovery from various musculoskeletal injuries, both acute and chronic. Central to the efficacy of shockwave therapy is the understanding of two fundamental concepts: shockwaves and mechanotransduction.
🎧 Prefer to listen? Click here.
Shockwaves are acoustic waves characterized by rapid pressure changes. They are composed of very high-pressure waves followed by low-pressure waves and serve as the active agent in eliciting tissue-specific responses through mechanotransduction. There are many different effects of shockwave that help with tissue healing and regeneration along with pain relief. Some of these include; angiogenesis, production of nitric oxide, chondrocyte protection, stimulation of bone metabolism, increasing lubricin production, and changes in the levels of Substance P.
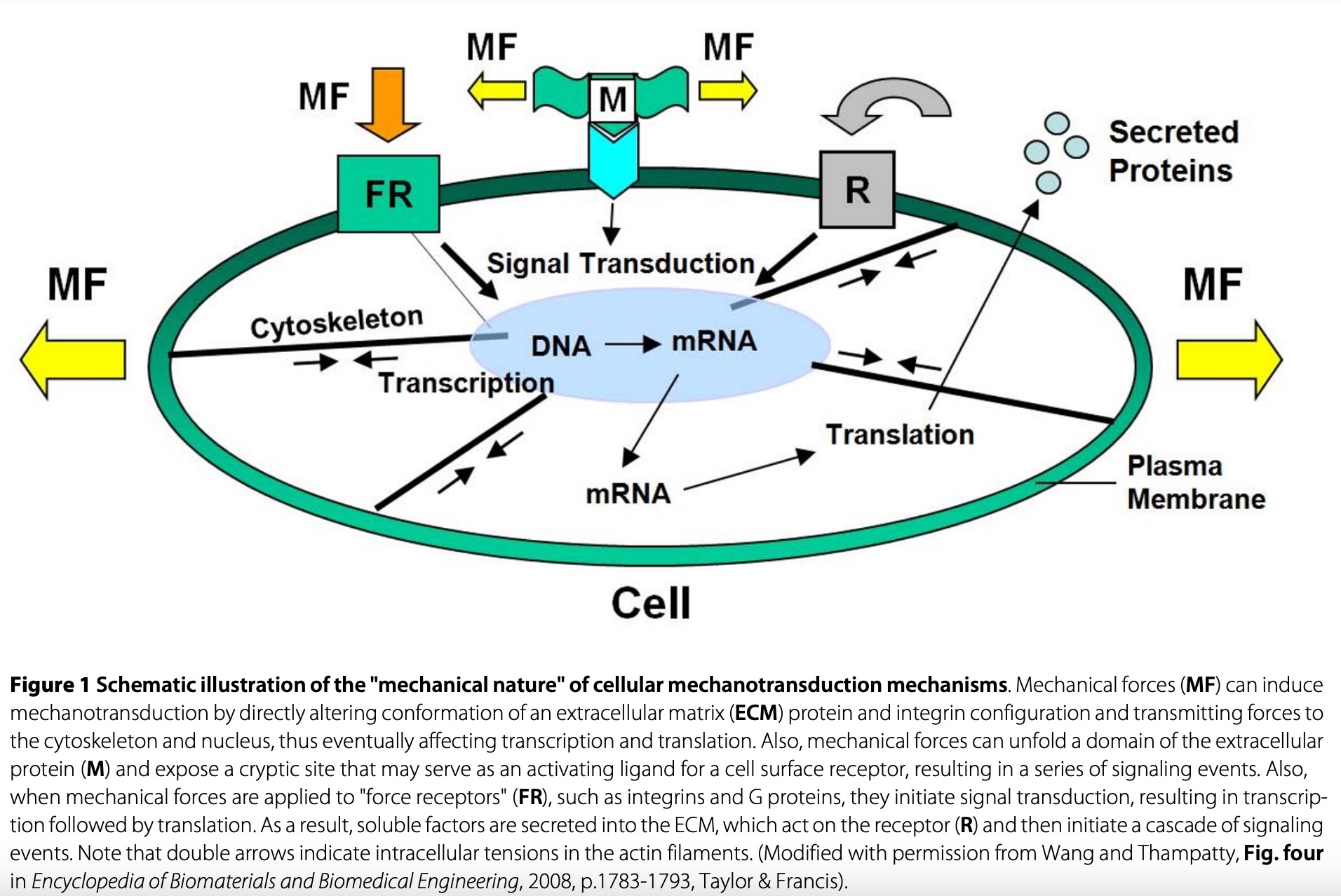
Mechanotransduction is a process in which mechanical energy is converted into biologic responses within cells. It involves physical stimuli and biological reactions, which ultimately influence tissue healing and regeneration. Mechano-sensitive cells include but are not limited to; osteocytes, chondrocytes, tenocytes, fibroblasts, and stem cells. These cells have mechano-sensitive receptors in the cell membrane and signal transduction occurs through molecular biologic pathways that are specific to each cell type.
There is a myriad of clinical research devoted to understanding specific internal cellular pathways of mechanotransduction that are beyond the scope of this blog. There is also the issue of how much energy it takes to initiate mechanotransduction and the limit of when too much energy can be detrimental to biologic tissue. The correct dosing for therapeutic shockwave does not have a simple answer and is discussed in more detail in this dosing blog.
Shockwave therapy in veterinary medicine is useful for addressing many clinical challenges. However, it is each practitioner’s responsibility to understand the basic principles of shockwaves and mechanotransduction and to practice the best medicine when applying shockwave therapy.
Here is a video summary of D’Agostino et al’s review paper titled “Shock wave as biological therapeutic tool: From mechanical stimulation to recovery and healing, through mechanotransduction.”
Below is a simplified diagram of cellular mechanotransduction mechanisms.

References:
- Wang, J. H., & Li, B. (2010). Mechanics rules cell biology. BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation, 2, 1-7.
- d'Agostino, M. C., Craig, K., Tibalt, E., & Respizzi, S. (2015). Shock wave as biological therapeutic tool: From mechanical stimulation to recovery and healing, through mechanotransduction. International journal of surgery, 24, 147-153.
- Dunn, S. L., & Olmedo, M. L. (2016). Mechanotransduction: Relevance to physical therapist practice—Understanding our ability to affect genetic expression through mechanical forces. Physical therapy, 96(5), 712-721.
ELvation Marketing Team
Combining sales and flexible customer support with many years’ in-depth knowledge of medical equipment we offer customized solutions to create value with long-term investments and medical supplies. ELvation’s strength lies in its ability to combine the apparently contradictory needs of improving the standards of patient care by providing high-quality medical technology and good corporate profitability. We have a special partnership with Richard Wolf GmbH as their long-term authorized Sales & Service Team for piezo shockwave systems.